What is in store for GEL and the prospects of the Georgian financial market
Professor emzar jgerenaia
Financial market becomes the main indicator and, at the same time, multiplicator of the world economy.
Derivatives, options, futures and daily trends of the exchange rate seem to be the vertex of the international market’s pyramid and, together with the general macroeconomic indicator, reflect the level of development or integration of the country’s economy. There are interesting phenomena in the functioning of exchanges as institutions, and the non-exchange trade is also developing at an unprecedented rate. At the same time, a very important event took place in the Georgian economy in November – the assets of “Bank of Georgia” were distributed at London Stock Exchange. Also in November the parliament was considering the monetary and credit policy of the National Bank as well as the guiding lines for 2007. What is happening at the world exchanges and what trends are there in Georgia?
Nasdaq decided to take up London
Stock Exchange, but …
American exchange operator Nasdaq offered 5,1 billion
USD for almost 75% of shares of London Stock Ex-
change (LSE). According to the press release spread in late November, the price of an ordinary share of LSE can be 12,43 GBP (23,47 USD, and the total offered sum – 2,7 billion GBP, i.e. 5,1 billion USD.
In case of LSE’s consent to this proposal, Nasdaq was planning this merger for the first quarter of the next year, but Londoners rejected it because of the sum’s smallness. On its part, London Stock Exchange found itself in a difficult situation because of a serious decrease in the number of clients. Besides, Euronext was taken up by New York’s largest and oldest platform, and now its total capital exceeds 25 billion USD. It is the largest trade platform and it is natural that it draws an increased attention of traders. Besides, serious American and European investment firms decided to set up a new exchange that will be of continental character trading at much lower commission both on American and European continent. The third factor is that all largest European and Asian platforms have merger trends. Londoners will not be able to avoid this globalization boom and, what is more, the price proposed by the American side is very impressive. Proceeding from this, London Stock Exchange is sure to be bought by Nasdaq, but a bit later, since Nasdaq no alternative in the concrete war for retaining of its positions.
In March 2006 Nasdaq offered LSE to sell its shares for 4,2 billion USD, but by Nasdaq’s decision this deal was not made, though LSE would not have agreed to this deal in any case. The Exchanges representatives declared that the indicated price of shares – 17,42 USD was lower than the real one.
Then Nasdaq started a planned purchase of LSE’s shares in May it became the largest shareholder of the oldest European Stock Exchange. As American companies point out, it possesses 25,1% of LSE’s shares and it is quite enough to block any other proposal and make them sell the platform to it.
London Stock Exchange founded in 1773 is one of the leading ones. It offers services in the sphere of capital attraction and security trading. At this Exchange unites more than 3 thousand companies, the total market capital of which makes up 4,1 trillion GBP. The Exchange holds the first place in the sphere of security trading both in Europe and the whole of the world. Such companies as General Electric, Boeing, Danone, General Motors and Nestle trade here.
The second largest US exchange operator Nasdaq specializes in trading in shares of high-tech companies, it has been working since 1971. The company’s capital makes up 3,6 trillion USD. This October they spoke about a possible merger of Nasdaq and Jasdaq Securities Exchange. This would give Japanese investors an opportunity of trading in shares of the international companies that are represented on the US stock market. However, it is a different time now – an unprecedented epoch of mergers has begun in the world and it has had an effect on other exchanges as well.
Deutsche Boerse admitted that its merger with Euronext has failed, but it was profitably purchased by New Yorkers.
Operator company of Frankfurt Stock Exchange Deutsche Boerse AG has rejected the merger with European exchange operator Euronext NV. According to the statement of Deutsche Boerse’s representatives, the exchange’s management admits that the planned merger with Euronext fell through and makes no other comments on this issue. Let us remind you that In June 2006 Euronext’s shareholders rejected the deal with Deutsche Boerse and gave preference to the deal with New Your Stock Exchange (NYSE). After that Deutsche Boerse increased the proposed sum to 10,6 billion USD (the sum off proposed by NYSE made up 9,96 billion USD) and was ready to make compromises, but it din not make Euronext’ s shareholders reconsider their position.
According to the terms proposed by NYSE, the deal will be fulfilled in shares and cash. Each share of NYSE will be converted into the shares of NYSE Euronext. The European operator’s shareholders will exchange their shares according to the following exchange rate: 1 share of Euronext for 0,980 share of the united company plus 21,32 EUR in cash. According to the terms of the deal, they expect that Euronext will pay dividends to its shareholders in its ordinary shares – 1 EUR for one share and the previously announced additional dividends – 3 EUR for one share.
By this merger, the first largest transatlantic operator NYSE Euronext will be formed. The cost of the deal makes up 9,96 billion USD.
Market capital of the united company will make up about 15 billion EUR (20 billion USD). It is planned to complete the deal at the beginning of 2007.
Euronext manages four European exchange spots – in Paris, Amsterdam, Brussels and Lisbon.
Chicago Mercantile Exchange purchases its colleague for 8 billion USD
Chicago Mercantile Exchange Holdings Inc.(CME) declared that it will purchase Chicago Board of Trade (CBOT) 8 billion USD. The name of the united company will be CME Group Inc and its head branch office will be in located in Chicago. According to the terms of the deal, exchange of shares will be carried out at the following ration: one share of CBOT will be exchanged for 0,3006 share of CME. It is supposed that the cost of the deal will not exceed 3 billion USD. In none of the shareholders sell their shares for cash, 69% of the new company’s shares will be in the hands of CME’s shareholders, while 31% – in the hands of CBOT’s shareholders. CME will issue about 15,9 million shares, the total cost of which will make up 8 billion USD. After completion of the deal, the Chairman of CME’s Board of Directors Terence Daffi will become the Chairman of the Board of Directors of the united company, and the Chairman of CBOT’s Board of Directors Charles Curry – Vice-Chairman of CME Group Inc. The deal will be completed in the first quarter of 2007.
Jasdaq and Nasdaq stock exchanges began to speak about the merger
Japanese stock exchange Jasdaq Securities Exchange and American Nasdaq Stock Market Inc speak about a possible merger, which would give Japanese investors an opportunity of trading in the shares of international companies.
According to the Japanese television company NHK, the exchanges will also consider the issue of distribution of shares in the Asian companies. Jasdaq’s representatives have confirmed that the exchange is holding negotiations concerning a possible merger with Nasdaq.
The world investments market is being united with the purpose of acceleration of the investments’ rate. Manny new markets, such as Moscow, Budapest and Warsaw exchanges, are involved in this mess.
Warsaw Exchange existed from the XIX century, but then it ceased its existence and was revived in the last decade. A serious growth started in the past three years, which was contributed by the government’s economic policy in the privatization sphere and formation as a joint-stock company. Today both public securities and shares and bonds of 29 large private firms are sold there.
What is going on in Georgia against the background of the world trend, how stock and currency exchanges are formed or why they are not formed, and how their nonexistence hampers the economic growth?
Georgian Stock Exchange at the end of the year
The last ¹89(674) trade session was held on 11/21/2006, 9 brokerage companies took part in it.
Number of deals: 56
Total volume of the deals (sec.): 47,579
Total cost of the deals (GEL): 234,294.58
On 17 November 2006 two non-exchange deals on the shares JSC “Borjommintskali” (BMIN) were fixed in the trade system of Georgian Stock Exchange. The volume of the first deal made up 572 903 shares, the cost – 1 117 160.85 GEL, while the price of one share – 1.950 GEL. The volume of the second deal made up 509 274 shares, the cost – 1 094 939.10 GEL, the price of one share – 2.150 GEL.
On 15 November 2006 a non-exchange deal on the shares JSC “Bank of Georgia” (GEB) was fixed in the trade system of Georgian Stock Exchange. The volume of the deal made up 96 179 shares, the cost – 2 079 389.98 GEL, while the price of one share – 21.62 GEL.
On 7 November 2006 a non-exchange deal on the shares JSC “Bank of Georgia” (GEB) was fixed in the trade system of Georgian Stock Exchange. The volume of the deal made up 846 864 shares, the cost – 6 258 324 GEL, while the price of one share – 7.39 GEL.
On 4 October 2006 the following non-exchange deals were fixed in the trade system of Georgian Stock Exchange:
– On the shares JSC “Akhmeta ghvinis qarkhana” (AGVQ). The volume of the deal made up 336 280 shares, the cost – 403 536 GEL, while the price of one share – 1.20 GEL.
– On the shares of JSK “Saqkabeli” (SAQK). The volume of the deal made up 632 907 shares, the cost – 817 942.08 GEL, while the price of one share – 1.311 GEL.
On 3 October 2006 a non-exchange deal on the shares JSC “Saqkalaqmshenproekti” (SQMP) was fixed in the trade system of Georgian Stock Exchange. The volume of the deal made up 242 013 shares, the cost –423 522.75 GEL, while the price of one share – 1.75 GEL.
On 26 September 2006 a non-exchange deal on the shares JSC “Bank of Georgia” (GEB) was fixed in the trade system of Georgian Stock Exchange. The volume of the deal made up 100 000 shares, the cost – 1 910 999.46 GEL, while the price of one share –19.11 GEL.
On 11 August 2006 a non-exchange deal on the shares JSC “Georgian United Telecommunication Company” (UTC) was fixed in the trade system of Georgian Stock Exchange. The volume of the deal made up 200 000 shares, the cost – 127 400.00 GEL, while the price of one share –0.637 GEL.
On 31 July 2006 a non-exchange deal on the shares JSC “Poti Gemtsasheni” (POGM) was fixed in the trade system of Georgian Stock Exchange. The volume of the deal made up 2 965 944 shares, the cost –949 102.08 GEL, while the price of one share – 0.32 GEL.
On 26 July 2006 a non-exchange deal on the shares JSC “Poti Gemtsasheni” (POGM) was fixed in the trade system of Georgian Stock Exchange. The volume of the deal made up 930 000 shares, the cost – 1 674 00.00 GEL, while the price of one share –1.8 GEL.
On 18 November 2006 a non-exchange deal on the shares JSC “Hotel Ajara” (HAJR) was fixed in the trade system of Georgian Stock Exchange. The volume of the deal made up 523 516 shares, the cost – 261 758.00 GEL, while the price of one share – 0.5 GEL.
From 7 November 2006 shares of JSC “Galt and Taggart Company” (GTC) are admitted to the trade system of the Georgian Stock Exchange.
From 1 November trade in the shares of JSC “Kutaisi Canning Factory” (KSK) will be recommenced.
From 7 November trade in the shares of 18 joint-stock companies will be recommenced.
From 1 November shares of the following companies are withdrawn from the trade system of the Georgian Stock Exchange:
1. Business Center Vazhaze (IAD)
2. Mandaria’s printing-house (KTST)
3. Mshenebeli-95 (M95)
4. Metekhi (MET)
5. Kaspicementi (KCEM)
This review of the stock market is another evidence of the fact that the only large client at the exchange is the Bank of Georgia, the management of which is implementing a serious capitalization program and the bank is a full-fledged joint-stock company, and that is the basis for their quick success.
Unprecedented not only in the Georgian economy, but in the whole post-soviet space
“Bank of Georgia” announces the price range, the results of the extraordinary shareholders’ meeting and the changes in the Supervisory Board.
On 17 November 2006, the leading Georgian full service bank JSC “Bank of Georgia” announced the price range of the first public offer (“offer”) of its shares issued in the form of global depository receipts. The price range of one global depository receipt was fixed between 15.00 USD and 17.50 USD. The offer makes up about 155 million USD, taking into account that additional issue of shares will be implemented. According to the price range, it is expected that at the beginning of the deal the bank’s market capital will make 350-425 million USD.
The offer includes the newly-emitted shares of “Bank of Georgia”, the emission of which was made with the purpose of enhancement implementation of new purchases and enhancement of operations. Offering of global depositary receipts will take place outside the US to the international institutional investors. The bank is planning to get permission so that global depository receipts should be put on the official list of the British listing regulation body and could be admitted to trading at London Stock Exchange. The bank will be the first Geoorgian company and the second bank in the CIS countries that will distribute its shares at London Stock Exchange after 1999.
The Chairman of the Supervisory Board of “Bank of Georgia” Lado Gurgenidze said: “Offering of shares at London Stock Exchange will help us to consolidate our position as the best full service bank in Georgia, attract additional sums from the international market of capitals and carry out diversification of the shareholders’ base. We have a distinct strategy and we consider this operation as an instrument for enhancement of the bank’s operations both in the region and abroad.”
Finally the trade was a success and the results surpassed all expectations. The demand was much higher than the supply and for this reason the price per share was fixed at the level of 18.5 USD. “Bank of Georgia” has become number one bank from the viewpoint of both capital and management.
The bank also announced the results of the extraordinary shareholders’ meeting that was held on 6 November 2006. The extraordinary shareholders’ meeting adopted increasing of the authorized capital by 5,552,210 shares, which is related to the aforementioned offer. For 14 November 2006 the bank’s authorized capital made up 25,335,619 shares, while the number of the issued shares became equal to 16,890,413.
The extraordinary shareholders’ meeting elected Alan Hirst and Nikoloz Enukidze members of the Supervisory Board. The Supervisory Board elected Mr. Enukidze the Chairman of the Supervisory Board and Mr. Alan Hirst – a member of the Compensatory Commission. Mr. Hirst joined the bank as a Non-Executive Director. He has a 24-year experience of work in the banking sector. He occupied a high post in “Citibank N.A.” and was the President of a closed joint-stock company “Citibank Russia”. Currently Mr. Hirst is a Non-Executive Director of JSC “Rosbank”. Since May 2006 Mr. Enukidze has been a special adviser to the Supervisory Board of “Bank of Georgia”. Before his coming to the bank Mr. Enukidze occupied a high posts in the leading Ukrainian investment bank, “Concorde Capital”, Moscow and London offices of “ABN AMBRO” and American telecommunication company “Global One Communications LLC”. London branch office of “ING Bank N.V.” was appointed main manager of the offer, “Bank Austria Creditanstalt AG” – joint manager, and the subsidiary bank of “Bank of Georgia” – “Galt & Taggart Security” –agent for the sale.
Financial results of “Bank of Georgia”
According to the account of the bank’s management, for 30 September 2006 the bank’s total assets made up 854.7 million GEL (from 31 December 2005 they have increased by 85.6%) and the total obligations – 717.7 million GEL (from 31 December 2005 they have increased by 94.4%). The bank’s net profit in nine months (for 30 September 2006) made up 17.3 million USD and increased by 96.0% against the previous year’s corresponding period. According to “Standard & Poor”, “Bank of Georgia” has ’B +/B’ rating with a stable prospect; according to “Moody” – ’3/N’ (foreign currency) and ’Baa3/P’ (local currency) with a stable prospect; according to “Fitch Ratings” – ’B-/B’ with a stable prospect.
It is not worth speaking of other exchanges since they have no effect on the investment system. Why?
The first reason is that foreign issuers do not come to Georgia and that is absolutely natural – we are not ready for them. The second one is that, except for banks, all large companies in Georgia, including public ones, are established in the form of Ltd, for example Georgian Railway. This, of course, is first of all ruinous for the companies themselves and that is why they have constant problems with management and growth. The railway is on the verge of decline and stoppage. At the same time it attracts capital for development and is in lack of transparency, and for this reason investors are avoiding it.
This kind of large enterprises hamper the formation of the financial market in Georgia.
There is a similar situation in many private sector’s enterprises, which are mainly represented by directors of one-person enterprises that do not want to sell even 1 percent or attract any solid investments. They remained in the old epoch and their enterprises are not developing. The market is in lack of issuers.
The Georgian business is moving in defiance of the world trends, that is why there will not be new jobs and the economy is confronting serious difficulties.
The currency is also facing difficulties since all parameters influencing its convertibility are deteriorating. Nevertheless, the National Bank is unprecedentedly strengthening it ruining export production.
Georgia’s economic indicators, inflation, trade deficit and employment are in lamentable condition. Against this background it is interesting what mechanisms contribute to strengthening of our national currency – lari in relation to the US dollar. We asked the Deputy Director of the Georgian Currency Exchange – Vakho Khomizurashvili to comment on this issue.
– First of all it results from the monetary and credit policy of the National Bank of Georgia aimed at withdrawal of monetary aggregates, i.e. the National Bank issues securities and withdraws monetary aggregates. In this case it introduced the obligatory norm of reserves (for the funds attracted to the banks). Contraction of money supply has a direct effect on the exchange rate. Currently the exchange rate is stable, lari is becoming increasingly strengthened, while the price index is rising catastrophically. If we make an analysis we shall see that the export potential has decreased, which has increased the trade deficit – in this situation import is dominating. That means that decreasing of the country’s GDP is taking place. Real product implies service on the produced output in the course of year and it is reflected in the previous period’s prices, which gives us an opportunity to see how much production has increased or dropped. The nominal product is reflected in current prices. It is impossible to establish quantitatively how much it has increased. The country’s GDP be grow, but it happens at the expense of price increase. In this case the GDP decreases, exporters’ expenses rise, produce that has not been sold will require additional expenses for storage and overstocking. This actually raises the prime cost of this produce. The way out is that the existing unemployment rate should be retained, since any country has a choice – strengthen its currency, retain the inflation rate or eradicate the unemployment problem. In our country the unemployment rate is quite high. There is the exchange rate inflation and inflation caused by the increase in the price index rate. There is the only way out – attraction of investments not from the state, but from private investors should take place as fully and quickly as possible. If such conditions are not made in time, improvement of the economic situation will become a more difficult task.
The investment environment should be really improved – there should be stimulative mechanisms for attraction of a long-term investment capital.
– What is implied by stimulative mechanisms?
– Introduction of changes to the Tax Code will be stimulating from the viewpoint of the fact that companies’ activities will become more transparent, which will contribute to issue of shares and public and subscription for them. Not a single foreign company will invest capital in enterprises and companies whose work is not transparent. Great attention is paid to the mechanism of investments’ protection, which implies the judicial system. Much attention is also paid to natural and artificial monopolies. When business is not in the equal situation, investors always refrain from making investments. A single and not a triple standard of actions should exist. When workplaces are not in profusion, the economy does not require money supply and the National Bank has to contract it. The population’s incomes do not rise, and, proceeding from this, the price index increases, while consumption diminishes. There is a macroeconomic formula, according to which money supply is multiplied by money turnover rate and that is equal to a country’s GDP multiplied by the price index. Reduction of money supply and increasing of the price index has a double effect on diminishing of the GDP.
The National Bank retains the exchange rate’s stability and does not release even limited information. The National Bank will be freed from this “compulsory policy” when amount of investments grows, and in this case a moderate exchange inflation will justified. Percentage of inflation will have commodity content, the demand for money supply will appear and that will be already justified.
Secrets of lari’s exchange rate
According to the world’s leading economic theories, the following factors have an effect on formation of the exchange rate of any currency, including lari:
1. Economic factors:
a) Interest rates (Central Banks’ interest rtes on credit resources).
b) Purchasing power of the currency, i.e., for instance, how much bread one can buy for one GEL or one USD.
c) Economic conditions:
– The dynamics of GDP growth, i.e. economic growth rate
– Unemployment rate
– Consumption and production indices
– The ratio of the budget deficit and foreign debt to the GDP
– The amount of the foreign trade balance’s deficit
d) Demand for capital and its and supply, i.e., in case of GEL, outside demand for GEL and our public and corporate securities.
e) Amount of tax tariffs
2. Political factors
– Character of the economic policy that is implemented by the government
– Criminal and international political security and stability
– The Central Bank’s policy on the open market
– Solidity and independence of the judicial system and property protection issues in the country
– Investment climate and the investment attraction dynamics
3. Human factors
– Level of qualified cadres
– Freedom of businessmen as well as the freedom to start and develop business
– Solidity of the democratic system and institutions
These are three main factors that have had an effect on the currency exchange rate in the three big world centers – USA, Great Britain and Japan since 1973, after floating rate of exchange was introduced. In spite of the fact that our currency is quasi-convertible, it conforms to the rules. It is a trivial issue for all financiers, let alone the National Banks and professional traders.
Moreover, it is a well-known fact that during President Bush’s meeting with representatives of the three machine-building giants they asked for assistance since the Japanese government artificially depreciates the yen and, by doing so, makes the export of their machines cheaper. As a result they are unable to meet competition with such cheap machines.
A similar war is being waged between China and the US. With the purpose of encouraging the country’s export, the Chinese government is artificially retaining the yuan’s exchange rate, etc.
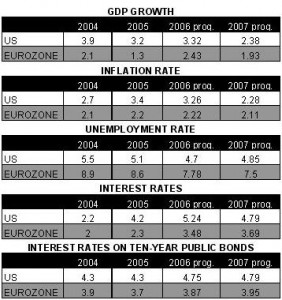
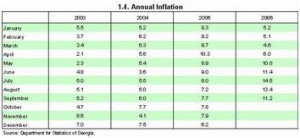
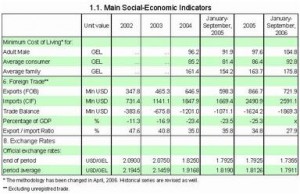
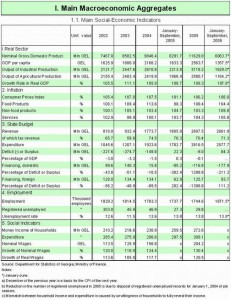
In Georgia all the abovementioned indicators affecting the exchange rate have serious problems: inflation – 11-13%, unemployment rate – 23%, trade balance deficit – 73%.
The foreign debt’s ratio to the GDP makes up 60%, the balance of payment deficit is chronically high and budget deficit makes up 7% of the GDP, the amount of inter-bank credits is high – 11-12 %, economic growth rate – 6-7%, GDP per head – 1 700 USD.
Conflict territories and the quality of the judicial system’s independence…
All indicators are unsatisfactory, but GEL’s exchange rate remains solid.
As a result we have a very expensive export, for instance that of wine. How our wine can be competitive if producers convert the expenses incurred in GEL into USD and EUR for obtaining the export price and get a higher prime cost than the price of Bordeaux in restaurants and bars. How can they meet competition? Why all investments in Georgia are mainly in the banking sector? Because credits are very expensive and banks have a guaranteed income, since they dispose of the circulating assets in a monopolistic way and impose a heavy load on production, including the agricultural sector.
Transfers in USD being received by the population from abroad, which are the source of their existence, make up a considerable part of the balance of payment. That is why, according to the data of the past two years, people lose 10 GEL per 100 USD when they exchange received sums for GEL. Added to this is the 12-14% inflation. It is easy to conceive how strained the social background is becoming and how the population’s purchasing capacity, i.e. the consumption index, is diminishing. That is why the mass of broad money in our country makes up 20% of the GDP, when in any normal country it is more than 100%.
What are we doing, monetary and credit policy it is, what ideology and purpose it has?
All over the word National Banks have one purpose, and it is a common truth – regulation of the optimal exchange rate and the inflation rate.
What about our National Bank?
In 2004-2006 GEL’s exchange rate in relation to USD strengthened from 1.8278 to1.7355. At the same time, according to the official data, the inflation rate has increased to 13% in comparison with last December’s level (according to experts’ calculations it has increased by 15%). According to the official data, the unemployment rate has decreased from 1 million 780 thousand to 1 million 630 thousand people, and the amount of GDP does not exceed 6 billion USD, which is quite a low indicator, if we say nothing of the consumer index and the export growth rate.
But what strengthens GEL’s exchange rate?
Representatives of the National Bank declared in the media that our currency’s exchange rate is more stable than that of USD and EUR.
Today the vexed issue is not that GEL’s exchange rate is not an optimal. Firstly, it impedes export’s development. Secondly, credits in the Georgian business space have very high interest rates and do not contribute to the development of export production and attraction of investments to the industrial and agricultural spheres.
Thirdly, as to the property form issue, in the public sector preference should be given to joint-stock companies and in the private sector – to their encouragement. Of course, the market will to put everything into place, but this applies to the highly-developed and organized market. Thus, both the monetary and credit policy of 2007 and the economic policy, on which this monetary and credit policy is based, should be conductors of this idea. We cannot proceed in defiance of the world trends.