World economy without Alan Greenspan or what is in store for us tomorrow
Emzar jgerenaia
The 79 years old bank wizard, after almost 19 years of domination, will leave his post next January for which he has already been elected three times, and where he has been forming the climate of the American and the world economy for 18 years.
What are the main factors that determined the outlines of the world economy in September, and what is the projection till the end of the year or for 2006?- natural disasters in the oil regions of the USA
– unstable political and economic situation in Europe and Japan
– uncontrollable growth of Chinese economy
Now about 80 million barrels of oil is produced in the world daily, from which 28 million fall to the share of the member countries of the international oil cartel – OPEC (Saudi Arabia, Qatar, United Arab Emirates, Iran, Venezuela, Algeria, Indonesia, Iraq, Libya, Nigeria, Kuwait) – eleven countries in all, producing eleven kinds of oil. Besides serious oil producers are: the USA, Norway, Great Britain, Russia, Romania, Azerbaijan, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, etc. The peak of oil production will be in 2010 – 90 million barrels a day. And the critical point will be reached in the year 2030, since the total oil reserves will last just for 40 years. According to the forecast of the American Oil Institute, the total volume of the reserves makes up 3 trillion barrels, but European analysts have made a more moderate forecast – 1 trillion barrels. And, besides, the oil fields that can be easily explored are running out, and it is necessary to switch to the development of deep layer reserves. That is why the increase of oil prices is logical and necessary so that this kind of hardly accessible fields would become attractive and profitable for investors.
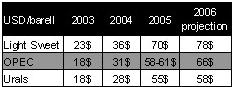
The dynamics of oil prices over the recent years is as follows:
At the same time the OPEC countries’ basket is characterized by lower indicators. It is natural that oil is the main component part of the world and Georgian economy. When it goes up in price, production costs rise not only because the price of gasoline, diesel fuel, kerosene increases, but also because plastic, chemical products, communication means, etc. rise in price as well. Thus, it is a multiplier of economic development and indicator at the same time. But the argument mainly takes place between oil producing and oil consuming countries concerning the issue of who will have more profits in the end. Presently the developed and developing countries mainly have the following pattern of end oil prices:
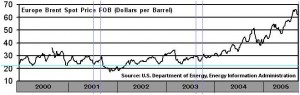
60% falls on the share of the consuming country in the form of taxes, 20% – of the processor and operator, and the remaining 20% – of the producer. Oil prices have increased by 100% compared to 2004, and if, for example a consuming country cuts the pressure of taxation by 20%, then in conditions of legal economy the price of the end product, for instance gasoline, will not change. The same works in Georgia as well. But an important source of budget replenishment in any country is taxation of fuel, that is why consuming countries cannot cope with this “booty” and prefer that the pressure should be exerted on producers that are weak and always concede. They concede by increasing supply and regulate the price. But today the situation is a catastrophic one, and, probably, this approach should be changed. Though when in April 2004 the prices reached $37 a barrel the experts called it a catastrophe, and now they got used to $67, and call the price of $62 stabilization.
Can “Katrina” and “Rita” solely be blamed for the increase of oil prices?
23% of the US’s oil refineries are located on the southern coast. In Taxes there are 26 refineries, of which 18 are located straight on the shore. In the Gulf of Mexico (where hurricanes originate from) they produce 1.23 million barrels a day. During Katrina this level dropped to 70%, and during Rita – to 50%.
In all, the US consumes 10 million barrels of gasoline a day, and produces 8.773 million barrels a day. In all, 15 million barrels of oil a day are delivered to the refineries for processing, or up to 20% of the world production. The country produces 5.7 million barrels of oil a day, but during the storm this indicator decreased to 4-4.5. Exxon Mobil Corporation and ConocoPhillips completely stopped production in the Gulf of Mexico.
By the end of September the total reserves of oil and oil products made up 1.0123 billion barrels, including strategic reserve at the disposal of the government – 699.2 million barrels. It is natural that a part of it was used in September and this stipulated a certain stabilization of prices. But after Rita they will start to replenish the reserves, which will increase the demand for oil and will have an inverse effect on the prices.
By the end of September, in the existing situation the following futures oil prices were formed on the US market:
Light sweet: November – 66.8, December – 66. 79, January – $67, For English sort Brent-$64.73, For OPEC basket – $58.9 a barrel, For natural gas – 12.594 per English fuel standard unit
At the end of September OPEC took a decision to increase daily production by 2 million barrels in order to help the US economy and regulate the prices. But, in spite of it, Katrina and Rita determine the climate on the oil market since they deliver a blow to the region where the US’s largest oil production and oil-processing facilities are located.
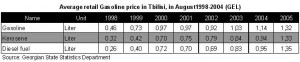
In January-September 2005, in the territory of the former Soviet Union the price of gasoline increased by 49%. Most of all gasoline prices have increased in Baltic countries, Ukraine, Armenia, and Russia. Georgia and other countries hold the second place.
In Georgia monthly gasoline consumption makes up 70 000 tons, annual – 840 000 tons (per 540 thousand cars, with average consumption of 11 liters for 100 km, and average run of 1700 km), diesel consumption – 450 000 tons, aviation fuel – 340 000 tons. Oil products are not used directly in the industry. That is why increasing of oil price made the basket of gods heavier by 25%, and in spite of strengthening of GEL the inflation rate increased by 13-15% in 2005 compared to 2004. Till the end of the year 630 million USD will be spent on gasoline importing. And if we add taxes to it, a considerable part of floating assets goes for fuel. Money deficit is observed in the economy and business stagnation is expected. Besides rising in price of bank resources in the world is added to it, and it is logical that in Georgia in conditions of small market purchasing capacity consumption and jobs will decrease. The rate of economic growth will become slower in the last quarter of 2005 and in 2006.
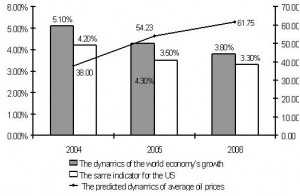
At the end of September the IMF published the World Economic Outlook and the projection intended for the annual meeting of the World Bank and the IMF. In the World Economic Outlook a forecast is given for the last quarter of 2005 and 2006 based on realistic oil prices and main economic trends. The indicators of economic growth are basic and important. The general picture in the world is a rather pessimistic one.
The indicator of GDP growth in 2004 was the highest after 1999, though it must be said that the IMF’s projection for 2005 was 4.4%, but the hurricanes have made some changes to it
Besides the hurricanes and oil prices, European problems have had an impact on it – non-ordinary elections in Germany, cabinet crisis in Italy and high cost of Euro.
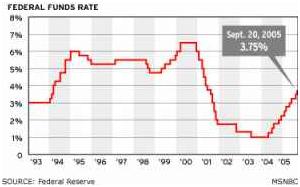
In response to it the Federal Reserve System has for the eleventh time increased the inter-bank credit rate by 0.25%, and, in the analysts opinion, the indicator of 3.75% will become 4.5 when Alan Greenspan will leave his post. Immediately commercial banks increased the credit rate for business and consumers. The money have become more expensive and the production growth stopped so that inflation would become controllable and the economy could withstand the increase of oil prices less oversensitively. In the experts’ opinion, this process will continue in 2006 as well. And besides the Congress has allocated 65 billion for the reconstruction of the affected regions, and President Bush is going to ask for another 200 billion for this purpose, which, in its turn, will contribute to production growth and appearance of new jobs.The indicator of decreasing of economic growth in the CIS countries is considerable – first of all in Russia, where, in spite of increasing of oil prices, the growth will make up 3.9% only, and if we take into account its economic relations with Georgia, here a serious decrease is expected as well.